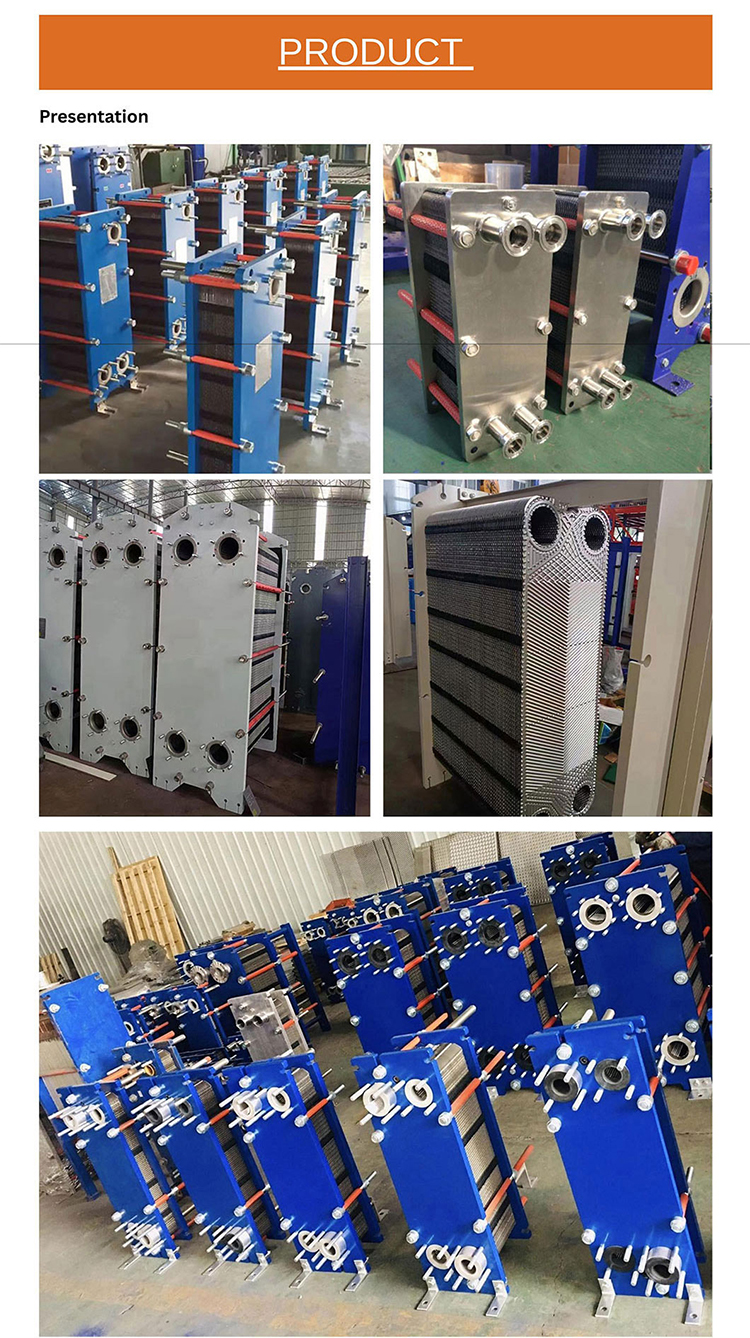
What is Plate Heat Exchanger?
A plate heat exchanger (PHE) is a type of heat exchanger that uses metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids, which consists of many plates stacked together in a frame. The plates are corrugated with gaskets at the corners and pressed together to form a series of channels where the fluids flow alternatively and exchange heat through the thin plates. It has a major advantage over a conventional heat exchanger in that the fluids are exposed to a much larger surface area because the fluids are spread out over the plates. Also, PHEs can improve efficiency through heat transfer by transferring energy between two fluids at different temperatures.
Advantages
Once you know what a plate heat exchanger is, it’s time to understand how it can benefit your boiler.
- Provides high value for your overall heat transfer. A flat plate heat exchanger typically has a U value much higher than a shell and tube heat exchanger or a spiral heat exchanger.
- It creates a compact design. Plate heat exchangers have the same thermal capacity as a shell and tube heat exchanger as much as five times its size. This is because of the combination of high-value heat transfer and the general compact configuration of the flat plates.
- Easy maintenance and cleaning. The plate heat exchangers can be taken apart, which allows for easy cleaning and maintenance of the equipment. The exchanger allows the addition or removal of plates to reduce heat transfer capacity.
- Control the temperature. Flat plate heat exchangers work well with small temperature differences among hot and cold fluids.
Disadvantages
Though there are some big advantages to plate heat exchangers, there are also some disadvantages when comparing them to other heat exchangers:
- Leakage:Plate heat exchangers are designed to allow plates and gaskets to be inserted between them. This increases the potential for leakage as gaskets age. Especially when compared to shell and tube or spiral heat exchangers.
- Higher pressure drops:Plate heat exchangers consist of narrow passageways for fluid to flow, which leads to a high heat transfer. This results in a higher pressure drop and a higher cost for pumping than shell and tube heat exchangers.
- Not beneficial for large fluid temperatures: Flat plate heat exchangers don’t work as well as shell and tube exchangers in cases where there’s a large temperature difference between two fluids.
- It doesn’t work well with very high fluid temperatures:The gaskets among plate heat exchangers can restrict temperature limitations.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.